12" x 12" PVD Stainless Steel Niche in Brushed Black by Alfi brand















Alfi brand 12" x 12" PVD Stainless Steel Shower Niche - 3 Finishes
$270
$232.31
Stainless Steel that's PVD processed is extra-durable, more corrosion-resistant, and more scratch resistant. These Alfi brand Niches are made of PVD Stainless Steel that's used only for the highest quality stainless steel products. These Niches are 12" x 12" overall and 4" deep. The complete explanation of the PVD process is included below under "About PVD Stainless Steel". Save $hundreds compared with constructing a tile niche. These extra-durable and extra good-looking niches are available in Brushed Gold, Brushed Black, and Brushed Copper.
Features
- Alfi brand PVD Stainless Steel Square 12" x 12" Shower Niche.
- All Stainless Steel construction finished in PVD Brushed Black, Brushed Gold, and Brushed Copper.
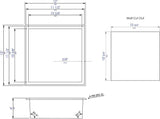
- Dimensions: 12" Wide x 12" High x 4" Deep. 3.7 lbs. Scroll through the images for the dimensions image with complete inner and outer dimensions.
- 1-Year Warranty.
About PVD Stainless Steel
PVD Stainless Steel
The Basics
PVD is an acronym for Physical Vapor Deposition. PVD is a vacuum coating process whereby a thin, durable film such as titanium nitride or zirconium nitride is deposited onto the surface of the Stainless Steel. Not only does it give the steel a decorative finish in Gold, Black, or Copper, but it also makes more durable, scratch-resistant, and corrosion-resistant.A more complete explanation of the PVD Process
1. PreparationThe substrate (often stainless steel) is thoroughly cleaned — usually with ultrasonic cleaning and plasma treatment — to remove oils, dust, and oxides. It's then placed inside a vacuum chamber.
2. Vacuum Creation
The chamber is sealed and air is pumped out to create a very high vacuum (around 10⁻⁶ to 10⁻⁹ torr).
This is necessary to prevent unwanted reactions and to allow free movement of particles.
3. Evaporation / Vaporization
The coating material (e.g., titanium, zirconium, chromium) is vaporized using one of these techniques:
• Arc evaporation – using electrical arcs.
• Sputtering – using ionized gas (plasma) to knock atoms off the material.
• Thermal evaporation – using heat to evaporate the material.
4. Transport
The vaporized atoms travel across the vacuum and move toward the cooler substrate.
Sometimes gases like nitrogen or argon are introduced to form compounds like titanium nitride (TiN).
5. Deposition
The atoms condense and bond onto the substrate, forming a thin, even, and very hard coating — often only a few microns thick (1 micron = 1/1000 m